Download: TIA Portal. Password Protect HMI. Let’s have a look into steps as shown below. Step 1: Enter in the TIA PORTAL environment. Select HMI screen size as explained in the article on how to create HMI screen. Totally Integrated Automation Portal (TIA Portal) enables complete access to the entire digitalized automation, from digital planning and integrated engineering to transparent operation. As part of the Digital Enterprise Software Suite, it joins PLM and MES in rounding out the comprehensive of-fering from Siemens for companies on the path.
- Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portals
- Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Page
- Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Login
- Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Sign In
Organization blocks (OBs) represent the interface between the operating system and the user program. Called by the operating system, they control cyclic and interruptdriven program execution, startup behavior of the PLC and error handling. You can program the organization blocks to determine CPU behavior.
Organization Block Priority
Organization blocks determine the sequence (start events) by which individual program sections are executed. An OB call can interrupt the execution of another OB. Which OB is allowed to interrupt another OB depends on its priority. Higher priority OBs can interrupt lower priority OBs. The background OB has the lowest priority.
Types of Interrupt and Priority Classes
Start events triggering an OB call are known as interrupts. The following table shows the types of interrupt in STEP 7 and the priority of the organization blocks assigned to them. Not all organization blocks listed and their priority classes are available in all S7 CPUs (see 'S7-300 Programmable Controller, Hardware and Installation Manual' and 'S7-400, M7-400 Programmable Controllers Module Specifications Reference Manual').
Type of Interrupt | Organization Block | Priority Class (Default) | See also |
Main program scan | OB1 | 1 | |
Time-of-day interrupts | OB10 to OB17 | 2 | |
Time-delay interrupts | OB20 OB21 OB22 OB23 | 3 4 5 6 | |
Cyclic interrupts | OB30 OB31 OB32 OB33 OB34 OB35 OB36 OB37 OB38 | 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 | |
Hardware interrupts | OB40 OB41 OB42 OB43 OB44 OB45 OB46 OB47 | 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 | |
DPV1 interrupts | OB 55 OB 56 OB 57 | 2 2 2 | |
Multicomputing interrupt | OB60 Multicomputing | 25 | |
Synchronous cycle interrupt | OB 61 OB 62 OB 63 OB 64 | 25 | |
Redundancy errors | OB70 I/O Redundancy Error (only in H systems) OB72 CPU Redundancy Error (only in H systems) | 25 28 | 'Error Handling Organization Blocks (OB70 to OB87 / OB121 to OB122)' |
Asynchronous errors | 25 (or 28 if the asynchronous error OB exists in the startup program) | ||
Background cycle | OB90 | 29 1) | |
Startup | OB100 Restart OB101 Hot Restart OB102 Cold Restart | 27 27 27 | |
Synchronous errors | Priority of the OB that caused the error | ||
1) The priority class 29 corresponds to priority 0.29. The background cycle has a lower priority than the free cycle. |
Changing the Priority
Interrupts can be assigned parameters with STEP 7. With the parameter assignment you can for example, deselect interrupt OBs or priority classes in the parameter blocks: timeofday interrupts, timedelay interrupts, cyclic interrupts, and hardware interrupts.
The priority of organization blocks on S7-300 CPUs is fixed.
With S7-400 CPUs (and the CPU 318) you can change the priority of the following organization blocks with STEP 7:
OB10 to OB47
OB70 to OB72 (only H CPUs) and OB81 to OB87 in RUN mode.
The following priority classes are permitted:
Priority classes 2 to 23 for OB10 to OB47
Priority classes 2 to 28 for OB70 to OB72
Priority classes 24 to 26 for OB81 to OB87; for CPUs as of approx. The middle of 2001 (Firmware Version 3.0) the ranges where extended: Priority classes 2 to 26 can be set for OB 81 to OB 84 as well as for OB 86 and OB 87.
You can assign the same priority to several OBs. OBs with the same priority are processed in the order in which their start events occur.
Error OBs started by synchronous errors are executed in the same priority class as the block being executed when the error occurred.
Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portals

Local Data
When creating logic blocks (OBs, FCs, FBs), you can declare temporary local data. The local data area on the CPU is divided among the priority classes.
On S7-400, you can change the amount of local data per priority class in the 'priority classes' parameter block using STEP 7.
Start Information of an OB
Every organization block has start information of 20 bytes of local data that the operating system supplies when an OB is started. The start information specifies the start event of the OB, the date and time of the OB start, errors that have occurred, and diagnostic events.
For example, OB40, a hardware interrupt OB, contains the address of the module that generated the interrupt in its start information.
Deselected Interrupt OBs
If you assign priority class 0 or assign less than 20 bytes of local data to a priority class, the corresponding interrupt OB is deselected. The handling of deselected interrupt OBs is restricted as follows:
In RUN mode, they cannot be copied or linked into your user program.
In STOP mode, they can be copied or linked into your user program, but when the CPU goes through a restart (warm start) they stop the startup and an entry is made in the diagnostic buffer.

By deselecting interrupt OBs that you do not require, you increase the amount of local data area available, and this can be used to save temporary data in other priority classes.
Cyclic Program Processing
Cyclic program processing is the 'normal' type of program execution on programmable logic controllers, meaning the operating system runs in a program loop (the cycle) and calls the organization block OB1 once in every loop in the main program. The user program in OB1 is therefore executed cyclically.

Event-Driven Program Processing
Cyclic program processing can be interrupted by certain events (interrupts). If such an event occurs, the block currently being executed is interrupted at a command boundary and a different organization block that is assigned to the particular event is called. Once the organization block has been executed, the cyclic program is resumed at the point at which it was interrupted.
Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Page
This means it is possible to process parts of the user program that do not have to be processed cyclically only when needed. The user program can be divided up into 'subroutines' and distributed among different organization blocks. If the user program is to react to an important signal that occurs relatively seldom (for example, a limit value sensor for measuring the level in a tank reports that the maximum level has been reached), the subroutine that is to be processed when the signal is output can be located in an OB whose processing is event-driven.
Linear Versus Structured Programming
You can write your entire user program in OB1 (linear programming). This is only advisable with simple programs written for the S7-300 CPU and requiring little memory.

Complex automation tasks can be controlled more easily by dividing them into smaller tasks reflecting the technological functions of the process or that can be used more than once. These tasks are represented by corresponding program sections, known as the blocks (structured programming).
See also:
I noticed you are very proficient regarding the subject so i decided to ask.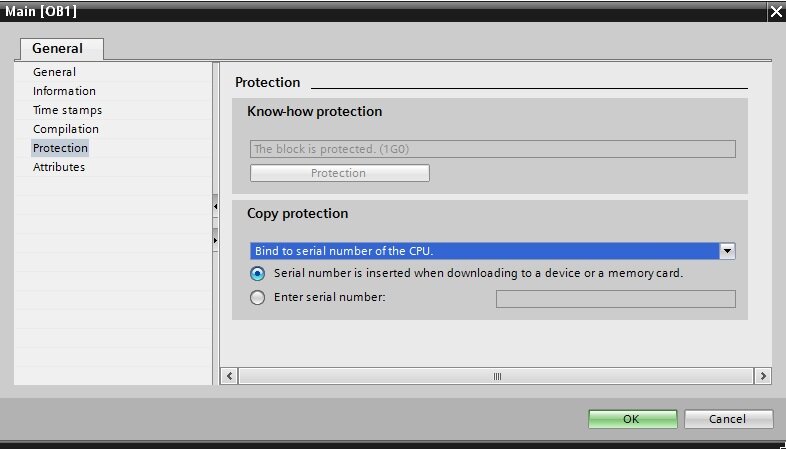
tip: block passwords in tia portal can ony be set in one session: if you close the block and reopen the button is greyed out.
tried using ollidbg but got dizzy.
Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Login
My other approach was using content comparison between the project/system/PEData.idx(plf) files before and after intoducing/changing the password.Passwords can be quite long so a brute force approach would be inconvenient.
Scenario 1: you have your designed software on your pc and you forgot the password of your ob1 function block.
Unlock Protected Blocks In Tia Portal Sign In
Scenario 2: you access a s7-1200 plc in a factory and need to modify the recipe parameters and add a fail-safe functionality to the existing program. The cpu is read/write protected and the function block is password protected. The whole soft is saved on the plc memory.
Here is a sample project with passwords all over it for a s7-1214 http://www.filehosting.org/file/details/390795/newp.zip
Most of the passwords are long so a brute force attempt would take alot of time.
something like Passw0rdPr)tect or PasswordProtected for the processor
the main function: I actually forgot this one, should be a long string
Kn0wH)w for the datablock
'password' for Bleeper function
pa55w0rd for ownedscl function
